Tongue & Lip Ties in Older Children
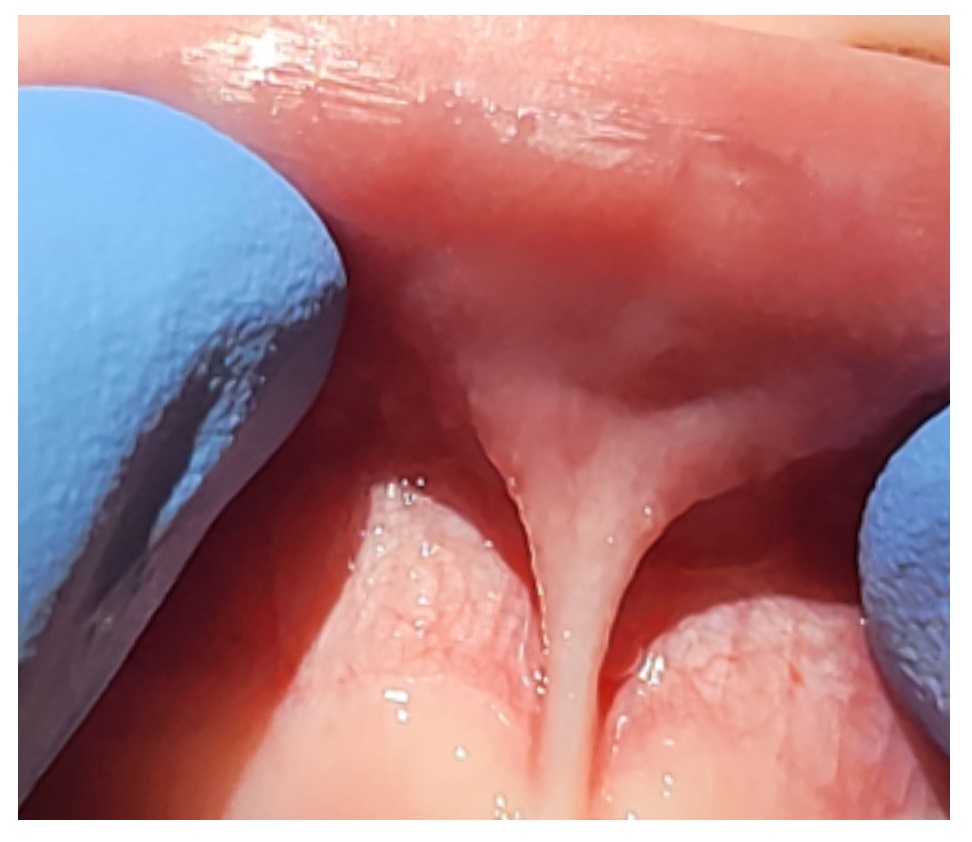
Children can have tongue ties and lip ties that affect function or anatomy. Regarding function, tongue ties can affect speech, swallow and eating. Regarding anatomy, tongue ties or lip ties can affect recession or contribute to space between teeth. As your child is learning to talk, you may notice difficulty with communicating and speaking, especially with making sounds such as d, l, n t, th, s and z. As a parent, you may also notice your child getting chronic sinus infections or ear infections.
Your toddler may also be experiencing difficulty with chewing and swallowing food, or even trouble cleaning bits of food off of the teeth with the tongue. Sleep issues, open-mouth breathing and snoring are also common signs of an oral restriction in little ones. At this stage, your child is learning important skills and functions that will serve them for the rest of their life. As a parent you might notice issues such as problems sleeping, a lisp or difficulty pronouncing certain sounds, challenges with activities such as licking a popsicle or playing a wind instrument. Parents may also be concerned about ADD and ADHD symptoms, which may be indirectly linked to sleep and brain function due to an oral restriction affecting their ability to breathe properly.
Older children tongue ties or lip ties symptoms

- difficulty with speech
- difficulty or limitations with eating, or difficulty licking an ice cream cone
- narrow dental arches, crowded teeth due to limited dental growth
- high arched palate (roof of mouth)
- myofunctional impairments such as poor swallow patterns, open mouth breathing, snoring
- gum tissue recession
- space between teeth (diastema)
Some older children and adults who have compensated for years may not realize they have had a lip tie or tongue tie. If there are functional or developmental concerns, your dentist might suggest a frenectomy or frenuloplasty procedure. This may help to restore function and improve range of motion or improve anatomy.
Is tongue-tie surgery necessary?
In some cases, tongue-tie isn’t severe enough to cause noticeable symptoms. Infants and young children who have tongue-tie but don’t have problems with feeding, swallowing or speaking may not need treatment. If your child has tongue-tie and has trouble feeding, their healthcare provider can perform a tongue-tie surgery in which they cut their lingual frenulum. This is called a frenectomy (also known as frenulectomy, frenotomy or tongue-tie division). It’s often performed without sedation on infants. Tongue-tie surgery causes minimal discomfort for infants.
How are tongue ties and lip ties treated in older children?
After a complete exam and consultation, our dentists can discuss which procedure is best indicated on a case-by-case basis. Most of the times we recommend a LightScalpel CO2 laser. The procedure is well tolerated by children and adults. A frenectomy or frenuloplasty is performed to release the tight frenum attachment.
Conclusion
Tongue and lip ties in older children can lead to a range of functional and anatomical issues, such as difficulty with speech, eating, and breathing. The severity of the condition determines whether treatment is necessary, but a frenectomy or frenuloplasty procedure can help to restore function and improve range of motion or anatomy. Aftercare is crucial to ensure the best possible healing results, including tongue retraining and continued care with a myofunctional therapist or speech language pathologist. Though there are associated risks and complications, the procedure is generally well-tolerated by children and adults, and recovery is expected to be smooth.
The issue is that tongue-ties cause not just poor weight gain or nursing pain – the two items traditionally seen by providers to be related to ties, but can cause many issues in infancy, childhood, and even into adulthood. Reflux, gas, colic, coughing or choking while eating, hiccups (more than once a day), unable to hold a pacifier, spitting up, mother’s nipple distortion or damage, trouble taking a bottle, and poor sleep quality, can all be related to a tie. So the first step is figuring out what current symptoms the child has, and if it’s affecting child or family’s quality of life. Because they usually do not stretch out or go away.
At this stage of development your baby may or may not be breastfeeding. Around six months, your pediatrician will advise you about how to introduce foods other than breastmilk or formula. Your baby will start to make babbling sounds, crawl and develop motor skills. Sleep and feeding patterns are changing.
Many, if not all, of these developmental milestones and processes can be affected by an oral restriction. As a parent, it is important to know the signs and symptoms of oral restrictions so you can communicate them to your healthcare provider who knows about tongue tie.
As your child is learning to talk, you may notice difficulty with communicating and speaking, especially with making sounds such as d, l, n t, th, s and z. As a parent, you may also notice your child getting chronic sinus infections or ear infections.
Your toddler may also be experiencing difficulty with chewing and swallowing food, or even trouble cleaning bits of food off of the teeth with the tongue. Sleep issues, open-mouth breathing and snoring are also common signs of an oral restriction in little ones.
At this stage, your child is learning important skills and functions that will serve them for the rest of their life. As a parent you might notice issues such as problems sleeping, a lisp or difficulty pronouncing certain sounds, challenges with activities such as licking a popsicle or playing a wind instrument.
Parents may also be concerned about ADD and ADHD symptoms, which may be indirectly linked to sleep and brain function due to an oral restriction affecting their ability to breathe properly.
Unfortunately, an alarming percentage of children aren’t getting the nightly rest they need to thrive.
In the last ten years, sleep problems have tripled across the globe and if kids are not sleeping well, then you as a parent aren’t either. Thankfully, there is a lot we can do to improve your child’s sleep.
Tongue or lip ties can be associated with speech or orthodontic issues in older children. When the tongue is unable to move freely, a child may have difficulty producing certain speech sounds. The most common letters affected are R, S, L, Z, D, CH, TH, and SH, but other sounds are also difficult.
There is no guarantee that a tongue-tie will automatically create speech problems, just as there is no guarantee that a frenectomy will solve existing problems. Delayed speech is not a symptom of a tongue-tie. There are, however, recent studies that show speech improvements after frenectomy.
Working with a speech and language therapist is an important step towards helping your child learn to produce proper speech sounds, regardless of whether there are tongue restrictions or not.
Lip or tie surgery is virtually painless. This procedure commonly causes little or no pain in infants, so anesthetics are not usually required for children under six months of age. Laser surgery offers several advantages. This process is performed through an incision, which effectively minimizes bleeding and promotes healing.
Tongue tie can sometimes cause problems such as speech difficulties, difficulty eating certain foods and difficulty cleaning teeth. Some other problems are appearance-related, such as a wide gap between the bottom two front teeth, or a V-shaped notch in the end of the tongue.
Check with a speech and language therapist if more than half of a three-year-old child’s speech is not understood by people outside of the family, or if the child has difficulty licking an ice cream cone.

